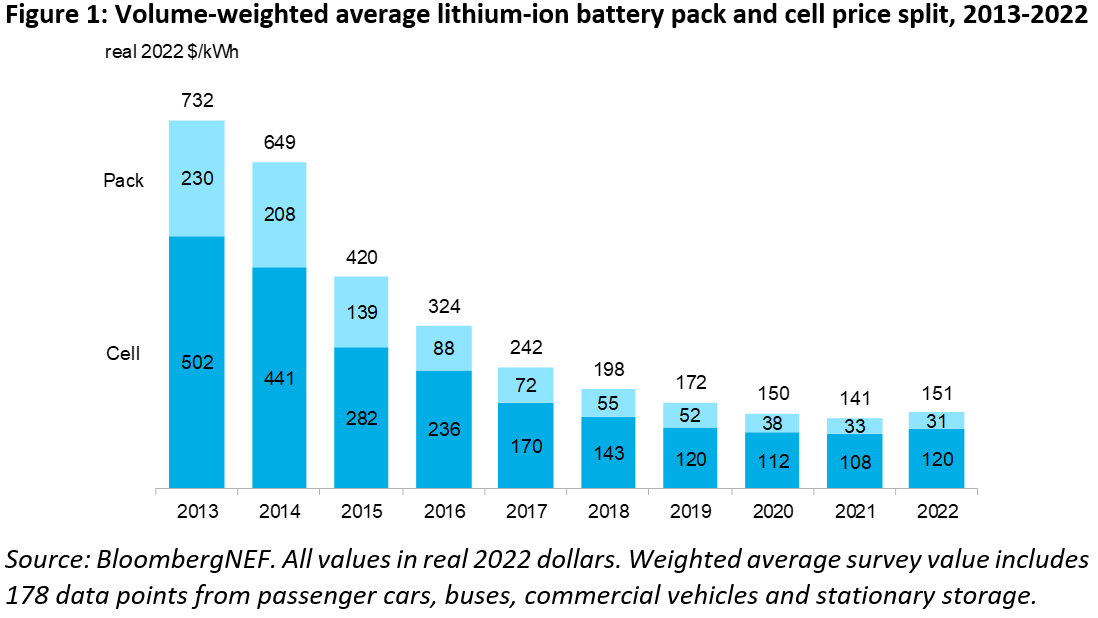
Battery pack prices increased by 7% from 2021 to 2022, according to BloombergNEF
No, it’s not an unexpected news. At all. But BloombergNEF is now outlining some precise figures on it. In its annual battery price survey the consultancy indeed found that lithium-ion battery pack prices increased by 7% from 2021 to 2022, up to $151/kWh. It’s presented as “the first ever increase in lithium-ion battery pack prices […]

No, it’s not an unexpected news. At all. But BloombergNEF is now outlining some precise figures on it. In its annual battery price survey the consultancy indeed found that lithium-ion battery pack prices increased by 7% from 2021 to 2022, up to $151/kWh.
It’s presented as “the first ever increase in lithium-ion battery pack prices since BloombergNEF (BNEF) began tracking the market in 2010”. Reasons are needless to mention (“Rising raw material and battery component prices and soaring inflation”). And demand will reach 603GWh in 2022, which is almost double that in 2021.
Forecasts? “Average battery pack prices will remain elevated in 2023 at $152/kWh (in real 2022 dollars)”. They should fall below $100/kWh by 2026. Before 2022, prices had dropped from well over $1,000 per kilowatt hour in 2010 to $141 per kWh last year.
BloombergNEF expects “next-generation technologies, such as silicon and lithium metal anodes, solid-state electrolytes and new cathode material and cell manufacturing processes, to play an important role in enabling further price reductions”.
Battery packs for BEVs at $138/kWh
Being more specific, the report reads that “For battery electric vehicle (BEV) packs in particular, prices were $138/kWh on a volume-weighted average basis in 2022. At the cell level, average BEV prices were just $115/kWh. This indicates that on average, cells account for 83% of the total pack price. Over the last three years, the cell-to-pack cost ratio has diverged from the traditional 70:30 split. This is partially due to changes to pack design, such as the introduction of cell-to-pack approaches, which have helped reduce costs”.
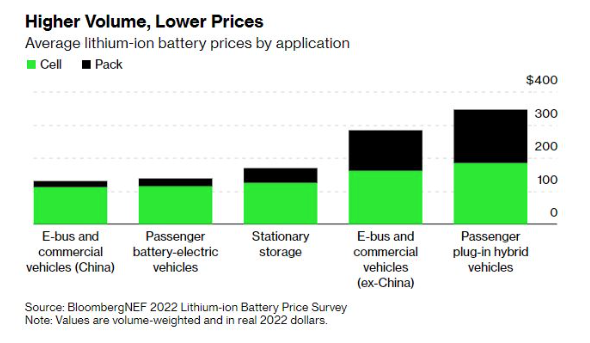
Battery pack prices were of course cheapest in China, at $127/kWh. Packs in the US and Europe were 24% and 33% higher, respectively. Higher prices reflect the relative immaturity of these markets, BloombergNEF says, the higher production costs, the diverse range of applications and battery imports. For the higher end of the range, low volume and bespoke orders push prices up.
What about LFP?
“Prices could have risen further in 2022 had it not been for the higher adoption of the low-cost cathode chemistry known as LFP, and the continued reduction of expensive cobalt in nickel-base cathodes – consulting says -. On average, LFP cells were 20% cheaper than lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC) cells in 2022. However, even low-cost chemistries like LFP, which is particularly exposed to lithium carbonate prices, have felt the bite of rising costs throughout the supply chain. LFP battery pack prices rose 27% in 2022, compared to 2021″.
LFP batteries have gained significant market share in the last three years, with BloombergNEF expecting them to account for around 40% of global EV sales this year.
Forecasts: battery prices to decrease again in 2024
BNEF expects “battery price to start dropping again in 2024, when lithium prices are expected to ease as more extraction and refining capacity comes online. Based on the updated observed learning rate, BNEF’s 2022 Battery Price Survey predicts that average pack prices should fall below $100/kWh by 2026. This is two years later than previously expected and will negatively impact the ability for automakers to produce and sell mass-market EVs in areas without subsidies or other forms of support. Higher battery prices could also hurt the economics of energy storage projects”.
Manufacturers turning to more aggressive strategies
Evelina Stoikou, an energy storage associate at BNEF and lead author of the report, said: “Raw material and component price increases have been the biggest contributors to the higher cell prices observed in 2022. Amidst these price increases for battery metals, large battery manufacturers and automakers have turned to more aggressive strategies to hedge against volatility, including direct investments in mining and refining projects.”
Yayoi Sekine, head of energy storage at BNEF, said: “Despite a setback on price declines, battery demand is still reaching new records each year. Demand will reach 603GWh in 2022, which is almost double that in 2021. Scaling up supply at that rate of growth is a real challenge for the industry, but investment in the sector is also rising rapidly and technology innovation is not slowing down.”
Kwasi Ampofo, head of metals and mining at BloombergNEF, added: “Lithium prices remain high due to persistent supply chain constraints and the slow ramp up in new production capacity. Additional lithium supply could ease the pressure on prices in 2024, while geo-politics and trade tension remain the biggest uncertainties for other key battery metal prices in the short-term. Resolving these tensions could help calm prices in 2023 and beyond.”







