Hungary – the future paradise for EV battery manufacturers?
Below, a report we published on the February 2024 issue of Sustainable Bus magazine, authored by Gellért Patthy, Magyarbusz [Info] Over the last years, many of the leader EV traction battery manufacturers and their suppliers chose Hungary as the location of their newly established manufacturing plants. This is in line with the goal of the Hungarian […]

Below, a report we published on the February 2024 issue of Sustainable Bus magazine, authored by Gellért Patthy, Magyarbusz [Info]
Over the last years, many of the leader EV traction battery manufacturers and their suppliers chose Hungary as the location of their newly established manufacturing plants. This is in line with the goal of the Hungarian government to become one of the main battery producer countries not only in Europe, but also at global level. We provide an insight into the background of the events and an overview about the companies involved.
As we all know by now, the future of the automotive industry – including buses – is electric, but Europe, the former frontrunner of the industrial revolution, now seems to struggle to take part in the global transition. One of the key products of the future are traction batteries, essential components of any electric – or even fuel cell powered – vehicles.
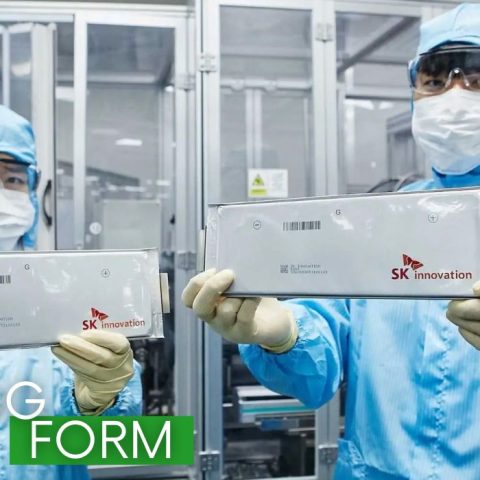
Márton Nagy, national economy minister of Hungary stated at a press event in September 2023 that the government has plans to build up an annual battery production capacity of 250 GWh in the next few years, which, according to him, would cover 35 percent of the European needs and would put the country to the fourth place worldwide, right after China, the United States and Germany. Indeed, by November 2023, battery production capacity in Hungary reportedly already reached 87 GWh/year, not including the newest SK Innovation plant, which is expected to begin production soon and to provide an additional output of 30 GWh/year alone when operating on full throttle.
While the center of battery R&D is typically located in the Far East, Europe is trying to stay competitive by hosting local factories of the industry leading companies. Within the European Union, Hungary puts a particularly high stake on EV battery plants, in the hope that it will find itself among the leading countries of an emerging industry within a few years.

A way to remain part of the game
Commitment to green mobility is not the only motivation for attracting large battery manufacturers to the small Central European country. As automotive industry gradually turns to more sustainable – practically electric – drivelines, fear of change (and the loss of the combustion engine market) also increases in Hungary, whose economy is currently highly dependent on automotive industry. Today, according the the estimations of the government, the conventional automotive sector is responsible for nearly 20 percent of the country’s total GDP, which comes not only from the large OEMs present at the country – namely Suzuki, Audi, Mercedes-Benz, Stellantis (Opel), with a new BMW assembly plant being under construction -, but also the many local and multinational industry suppliers settled in Hungary during the last decades. However, producing traction batteries in large amounts seems to be a good card to remain part of the game in the future as well.
For the above reasons, the establishment of factories related to the EV battery industry (including supplier products) enjoys huge financial and political support from the Hungarian government – a reason often mentioned by the battery manufacturers themselves when they are asked about their reasons why choosing Hungary as the location of their newest plants.
The central position of the country within the region, the local big car factories and the relative proximity of others in the neighbouring countries – such as Slovakia, Romania or even the Czech Republic – also contributes in making Hungary a considerable place for such investments.
The full EV supply chain
In almost every month in 2023, the Hungarian media could report on the announcement of the establishment of a new plant related to the EV battery industry. Márton Nagy, national economy minister of Hungary stated at a press event in September 2023 that the government has plans to build up an annual battery production capacity of 250 GWh in the next few years, which, according to him, would cover 35 percent of the European needs and would put the country to the fourth place worldwide, right after China, the United States and Germany. Indeed, by November 2023, battery production capacity in Hungary reportedly already reached 87 GWh/year, not including the newest SK Innovation plant, which is expected to begin production soon and to provide an additional output of 30 GWh/year alone when operating on full throttle.
It is also worth mentioning that not only battery cell and module producers, but also all participants of the whole supply chain, such as electrolyte, anode, cathode, aluminum/copper foil, separator foil and battery part manufacturers, as well as industrial waste recycling firms are welcomed by the Hungarian government, which is well demonstrated by the various recent local investments of these companies. Moreover, there are even plans for local lithium extraction, by exploiting geothermic deposits.
As automotive industry gradually turns to more sustainable – practically electric – drivelines, fear of change (and the loss of the combustion engine market) also increases in Hungary, whose economy is currently highly dependent on automotive industry. Today, according the the estimations of the government, the conventional automotive sector is responsible for nearly 20 percent of the country’s total GDP, which comes not only from the large OEMs present at the country – namely Suzuki, Audi, Mercedes-Benz, Stellantis (Opel), with a new BMW assembly plant being under construction -, but also the many local and multinational industry suppliers settled in Hungary during the last decades. However, producing traction batteries in large amounts seems to be a good card to remain part of the game in the future as well.
A hotspot of Eastern investments
EV battery cell and module manufacturers currently present at Hungary come from the Far East – namely South Korea, Japan, and, first of all, China. The supplier segment is also dominated by these countries, for whom setting up a local production base in a relatively cheap but well-located EU-member state provides an entrance to the European market. Some political concerns raise at European level, especially in case of China.
And where are all these batteries going, can we see them in e-buses? Well, although the products of some of these manufacturers, such as Samsung SDI or CATL can be found in electric buses too and some of the locally produced cells would be suitable for use in electric or fuel cell powered buses as well, at the moment most customers of the battery industry products produced in Hungary are coming from the passenger car business. Some of the OEMs representing the main customer market also operate in Hungary, while the local Hungarian bus industry – which is currently a shadow of its former glory, although some developments have been done the last years – plays a negligible role for now. The only exception is BYD, which operates (among others) a bus assembly plant in Hungary and uses its own batteries.
In below, we provide a slight overview about the EV battery producer companies which already operate manufacturing plants in Hungary or announced to do so in the near future. We also take a look at their products and manufacturing capacity.
BYD
An internationally well-known and respected Chinese company, BYD has special connections in Hungary. Its already mentioned bus assembly plant in Komárom started operations in 2017, and now is the only foreign-owned bus factory in a country which has a huge heritage in bus and coach manufacturing.
BYD is also the current leader of the local e-bus market, but buses will not be the only vehicles that roll off Hungarian production lines.
On December 22, 2023 it was officially confirmed that BYD will build up its first European electric passenger car assembly plant in the city of Szeged, in the southeastern corner of Hungary. Last but not least, BYD’s battery business branch also plans to establish a manufacturing unit in the country, namely at Fót, in the northeastern agglomeration of Budapest.
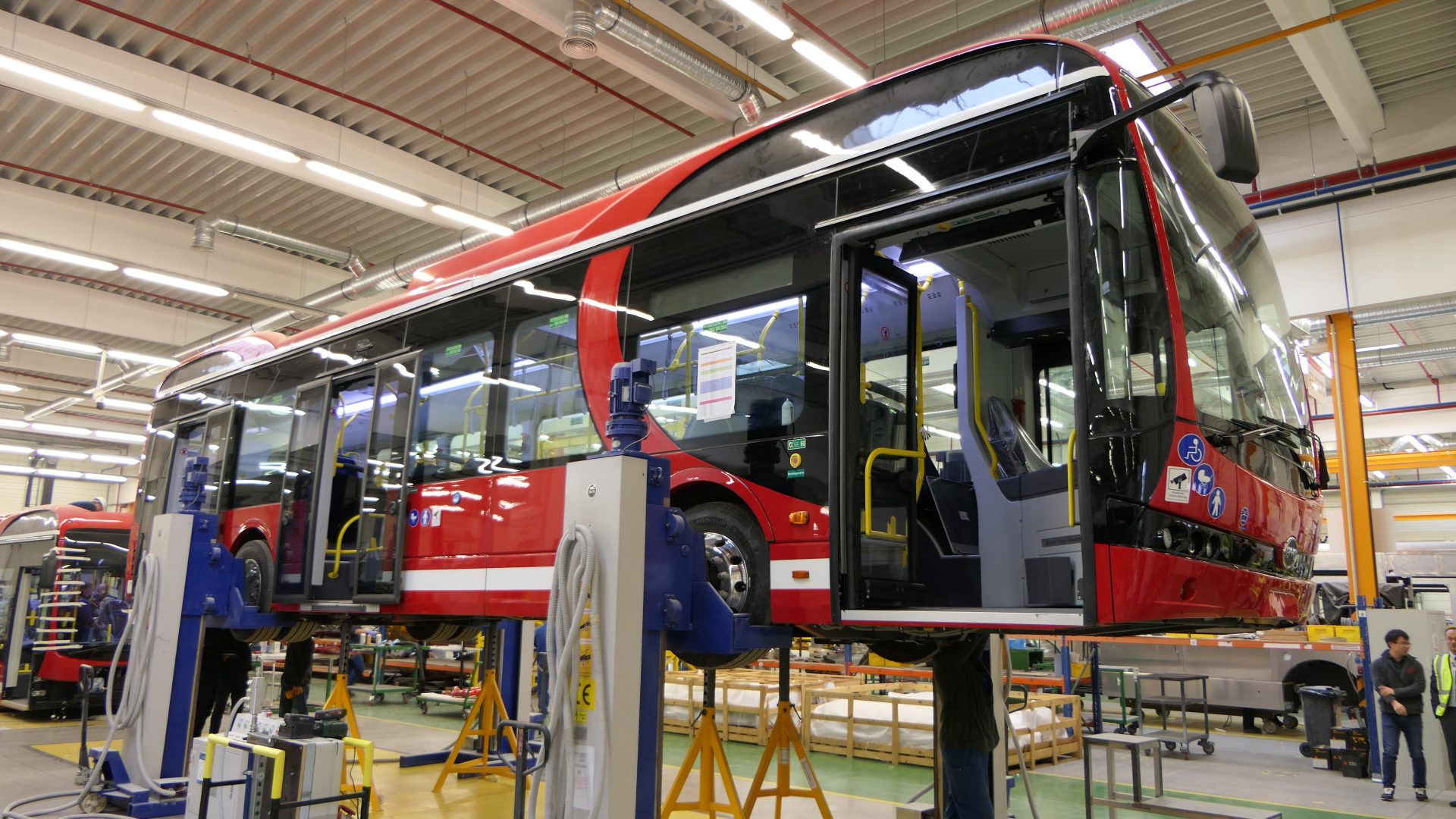

It is important to note that unlike the previously mentioned EV battery makers, BYD would not manufacture battery cells in Hungary, but would establish an assembly plant for battery packs, without the use of harmful chemicals. When officially announcing the new plant’s arrival in June 2023, Péter Szijjártó, minister of foreign affairs and trade of Hungary stated that the total value of the investment is 10 billion HUF (nearly 27 million euros), with a financial support of 1 billion HUF from the Hungarian government.
The initial plans include a workforce of 100 people. The battery modules and packs would be assembled from cells based on LiFePO4 chemistry, which themselves would come to Fót from other BYD facilities. The Hungarian-assembled batteries are intended for use in various electric vehicles, including e-buses. However, neither the exact vehicle types, nor the factory’s planned production output has been confirmed yet.
CATL
The largest EV battery maker of the world for six consecutive years by now (according to the 2022 report of the SNE Research market research and consultant company from South Korea), CATL is a well known supplier of many electric cars and buses worldwide. The Chinese industry giant is also considered to be one of the most important company in the Hungarian economy in the future. Although not operating yet, it is already decided and officially announced that CATL will establish a huge battery cell manufacturing plant in Debrecen, the second most populous city of Hungary. This will be the second battery manufacturing base of the company outside China, after commissioning the first such unit in Erfurt, Thuringia, Germany.
The project, which is the biggest greenfield investment to date in Hungary with its total value of 7.34 billion euros, enjoys great support from the Hungarian government, in order to create an estimated 9,000 jobs locally.

According to the available industry news, CATL’s Debrecen plant will produce NMC cells in prismatic and cylindrical format. Production output in the first phase will be an impressive 40 GWh/year, with plans already announced to increase it to even 100 GWh/year in the near future. Trial production is planned to start at the beginning of 2025.
Modules and cells produced at the Debrecen factory will appear in electric models of approximately 30 different car manufacturers, including BMW, Daimler, Volkswagen, Toyota, Volvo and Tesla.
CATL traction batteries are also widely used by e-bus manufacturers, among others the world’s largest bus and coach manufacturer Yutong and the Hungarian brand Ikarus.
EVE Power
In May 2023, another major battery industry investment was officially announced on the Hungarian media: EVE Power, another powerful Chinese participant of the EV battery industry, will establish its first European production plant in Debrecen.
It will supply 6th-generation cylindrical lithium-ion battery cells, most probably in a 4695 format, for the future BMW battery module assembly plant located also in the same city, with a massive production capacity of 28 GWh/year.
The total value of the investment exceeds 1 billion euros (from which 37.5 million euros come from the Hungarian government as financial support). The factory is expected to start operating in 2026, with a workforce of more than 1000 people.
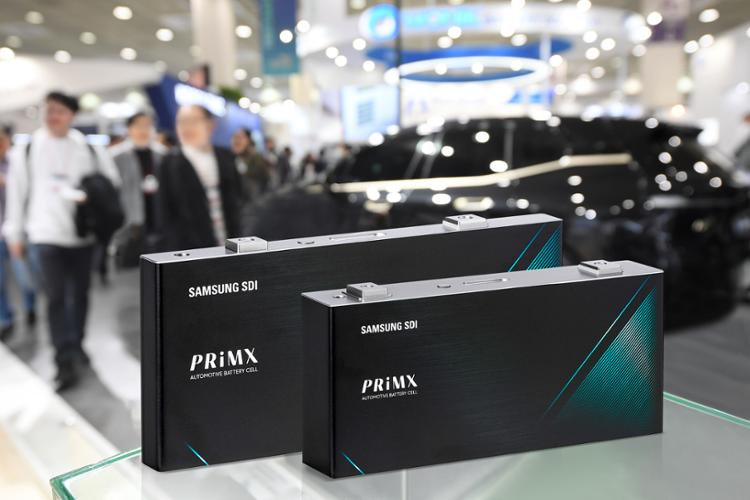
Samsung SDI
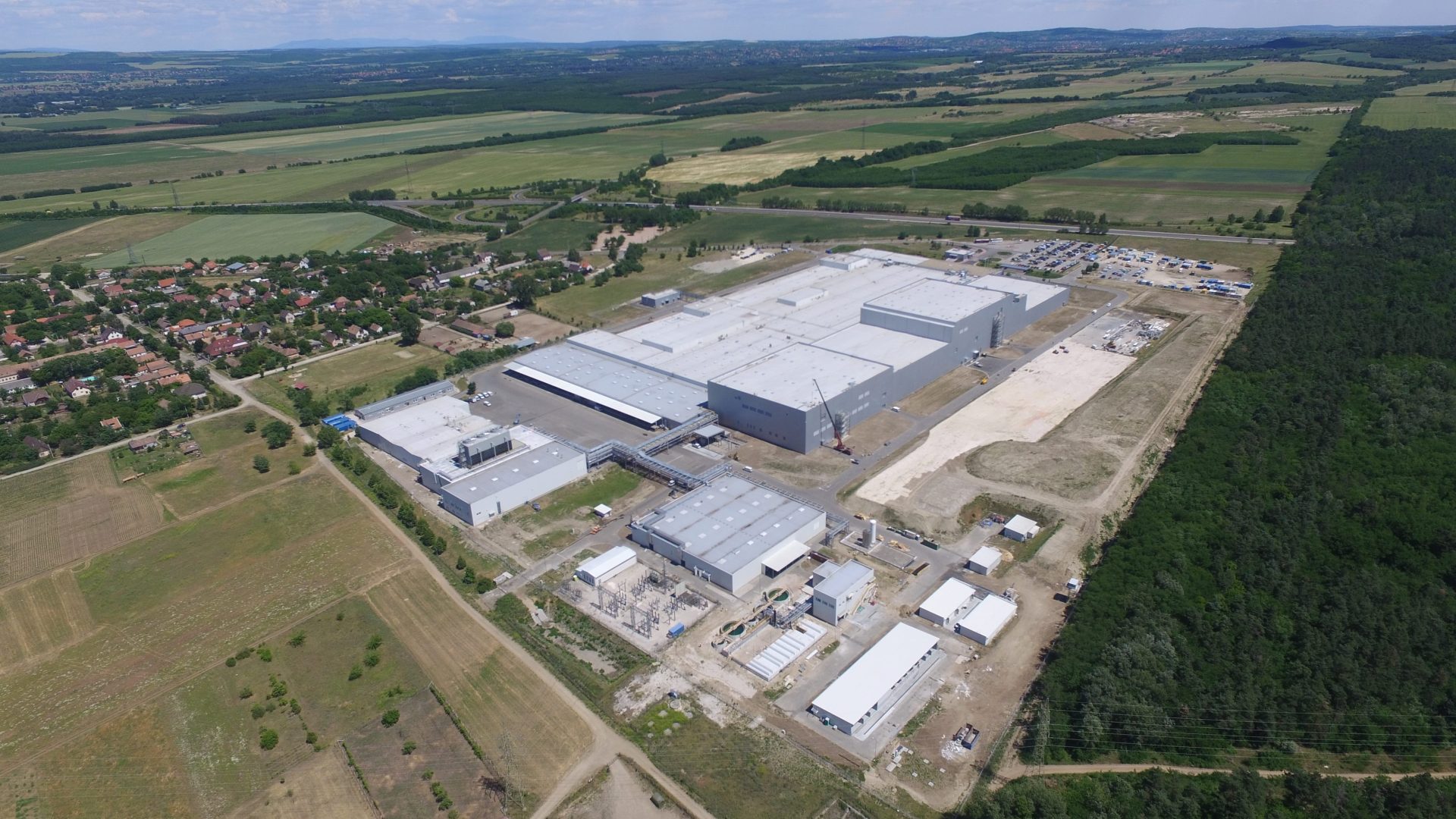
Samsung SDI, one of the leading EV battery cell producers worldwide, can be considered as a pioneer of the traction battery industry in Hungary, as it started to construct its first traction battery plant in the country as early as 2016, located at Göd (sometimes written as „Goed” in the international media), a town about 25 kilometers north of Budapest. In fact, it was a brownfield investment by converting Samsung’s own former cathode ray tube factory, which was closed two years before, due to the market loss of the technology.
The new battery plant’s inauguration ceremony was held in 2017, quickly followed by a further expansion investment of 1.2 billion euros in the same year. As a result, the second unit was completed in 2019 and reached full production capacity (more than 6 million cells/month) by January 2022. By now the total manufacturing output increased to 40 GWh/year.
Prismatic battery cells produced here are are used in electric cars of BMW, Volkswagen and Stellantis.
The Hungarian plant will also supply sixth-generation P6 prismatic NCA cells for Hyundai Motor’s electric vehicles dedicated for the European market, starting from 2026.

In January 2023, there were reports that Samsung SDI would expand its operations in Hungary with a new production plant, with a similar output as the previous two. According to the rumours, this facility would produce 46120-type cylindrical cells, to be used exclusively in BMW cars – more precisely, the planned new manufacturing unit is expected to supply the also recently-announced BMW battery module assembly plant in Debrecen, Hungary.
From an e-bus perspective, Samsung SDI cells are used in the traction battery packs of Akasol (since 2021, BorgWarner), which itself is a supplier of Mercedes-Benz, Van Hool and Industria Italiana Autobus. The current Hungarian market leader Credobus will also use these packs in its all-new zero emission bus family, scheduled to be introduced in 2024. Also, battery technology of Samsung SDI is used in Webasto batteries, which can be found for instance in Otokar e-buses.

SK Innovation
Another major player from South Korea, battery industry giant SK Innovation operates three plants in Hungary by now. Two of them are located in Komárom – the same northwestern Hungarian town which is the home of BYD’s now-only European bus assembly plant -, while the newest, third unit recently started operation at Iváncsa, with an almost twice higher production output than the former two combined.
The original Komárom plant – which was the first European plant of the company, operating since the end of 2019 – produces third-generation pouch battery cells, with a manufacturing capacity of 7.5 GWh/year, on a total of five assembly lines. Capacity was increased by a further 9.8 GWh with the commission of the second manufacturing unit in 2022, which has a capability to be scaled up to even 16 GWh/year. The number of employees, originally 475, was also boosted by another 1,000. These two plants mainly supply battery cells for the electric vehicles of Daimler and Volkswagen.
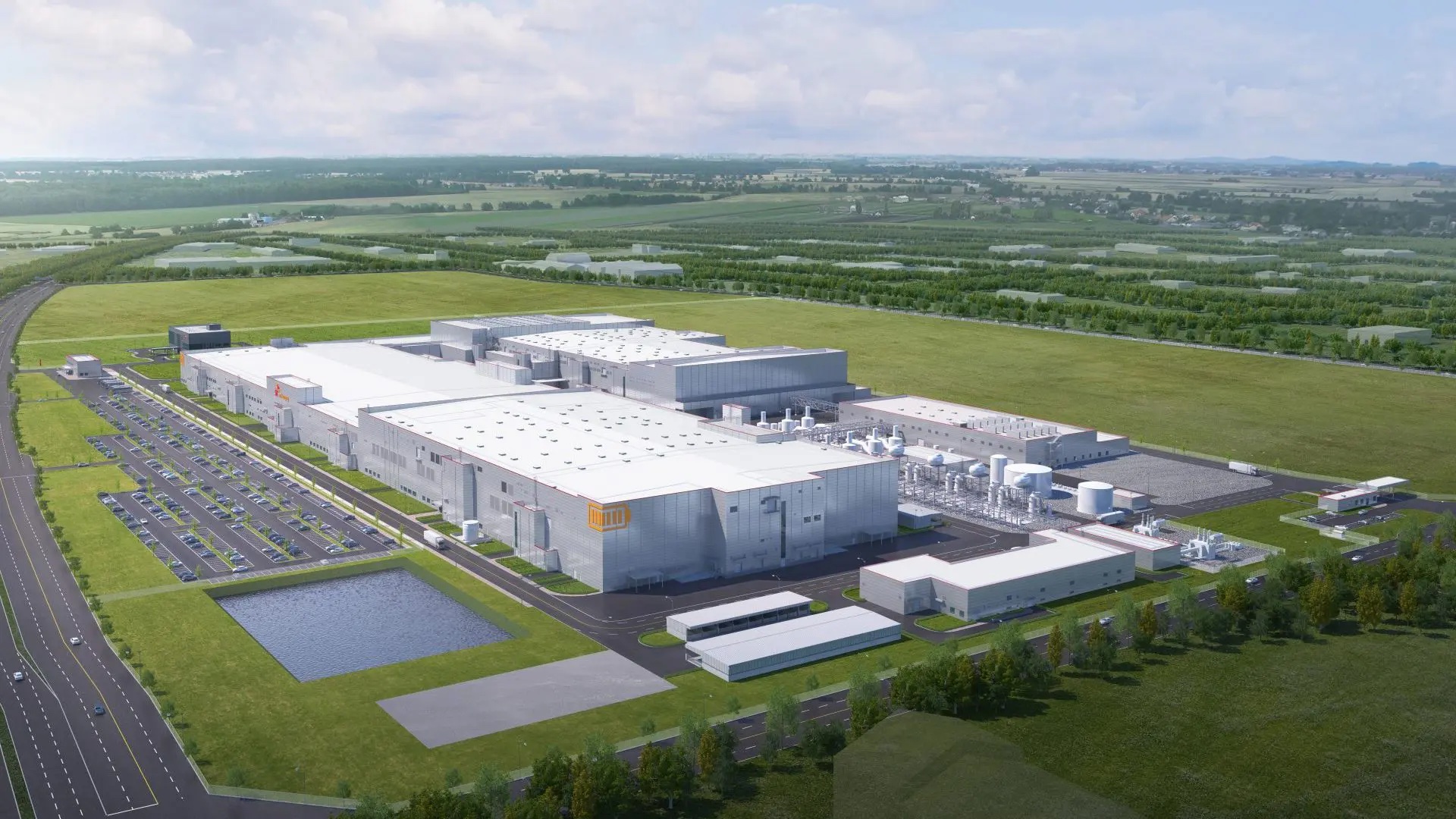

The company’s newest, third factory in Hungary will operate at Iváncsa, a small town 51 kilometers southwest of Budapest. Just in order to perceive the dimensions and the importance of this project, at the time of its official announcement in early 2021, it was considered to be not only the largest green field investment in the history of Hungary up to that point (value: 1.9 billion euros), but also the largest EV battery plant in Europe.
Although the factory buildings are ready and production is expected to start soon, various works are still remaining around the plant, such as the construction of road and industrial railway connections, and the set up of service infrastructure. When operating at full capacity (expected from mid-2024, although the plant’s full completion is only scheduled for 2028), the facility will provide an annual production output of 30 GWh, with a workforce of 2,500 people. SK Innovation has ambitious plans to increase its global annual production output to 125 GWh by 2025 and to 500 GWh by 2030, in which they assign a large role to their Hungarian manufacturing capacities, along with their facilities in South Korea, China and the United States.
SK Innovation’s Hungarian plants were also involved in some safety issues: in June 2023, dozens of workers experienced sickness during the construction of the Iváncsa plant after inhaling an unknown chemical. This incident was also widely reported in the local media.
Sunwoda
At the end of July 2023 Sunwoda also officially announced that it would build a new battery plant in Hungary. The Chinese company’s first European manufacturing facility will be established in Nyíregyháza, a city in the northeastern region of the country, with an initial investment of 245 million euros. However, in medium to long term this may increase to even nearly 1.5 billion euros, creating more than 1,000 jobs locally. The size of the planned production capacity and the type of battery cells to be produced have not yet been announced. Construction of the factory will start in 2024, with production is expected to begin at the end of 2025.
Sunwoda is considered among the top 10 EV battery manufacturers worldwide based on market share, and is a supplier of Volkswagen, the Renault-Nissan group and Dongfeng, among others. However, customers of the products to be manufactured in Hungary have not yet been named, it was only communicated that the new plant will work for the “international market”.
To sum up, the building up of the new industry is well on its way in Hungary. The number of the settled companies is expected to increase even more in the near future, for example there are rumors about the possible arrival of Hangke Technology, another EV battery industry player from China.